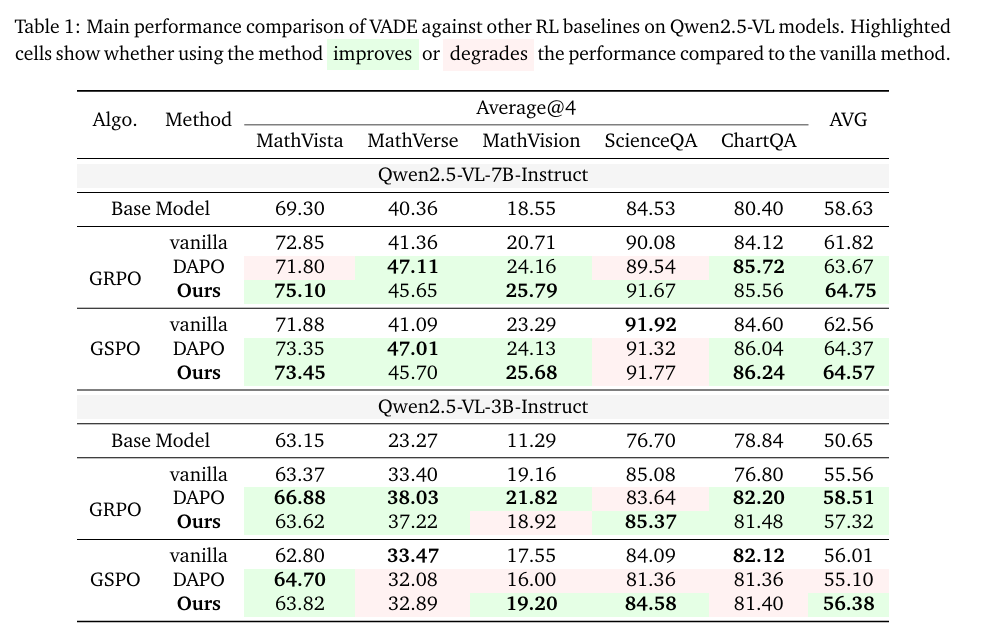
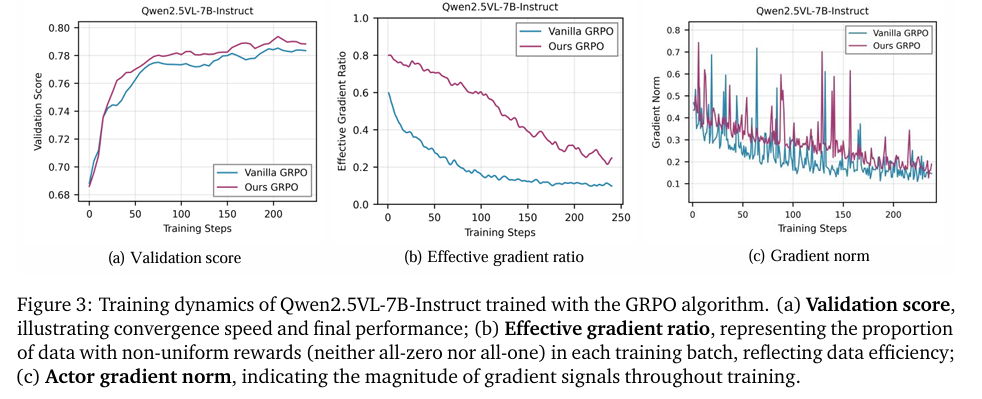
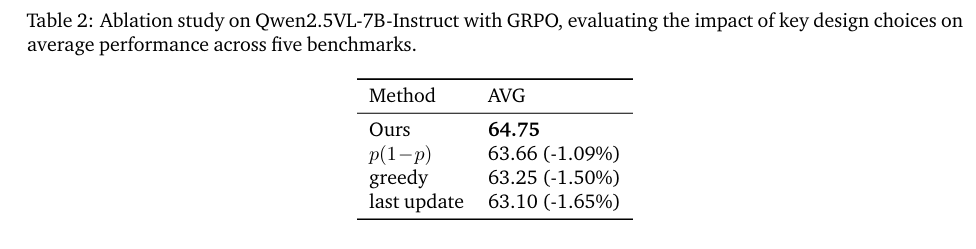
Method
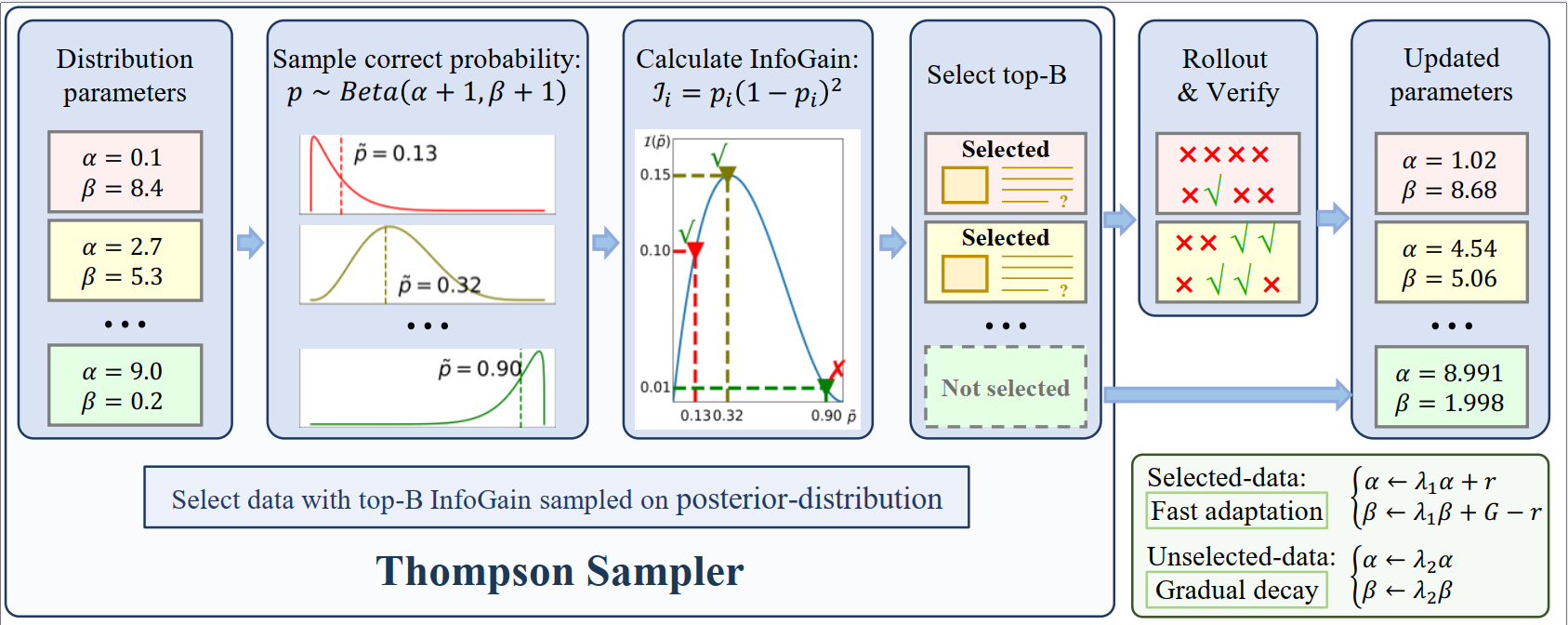
Overview of the VADE framework. Our method maintains distributions \(\text{Beta}(\alpha_i + 1, \beta_i+ 1)\) for each sample to enable online difficulty estimation. Through Thompson sampling and InfoGain \(\mathcal{I}_i = p_t(1-p_t)^2\) maximization, VADE dynamically selects informative batches for group-wise rollouts. The two-scale prior decay mechanism ensures estimates remain accurate throughout policy evolution.